Augmentation Rhinoplasty
Asian Rhinoplasty / Nose Implant
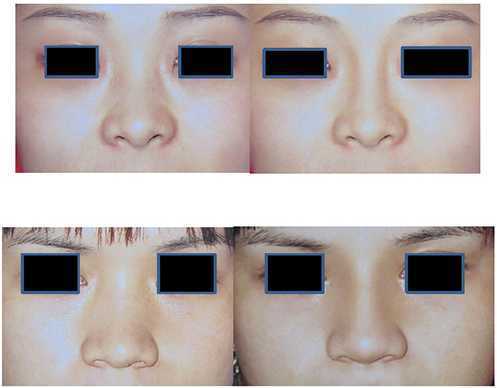
What is Asian Rhinoplasty?
Asian rhinoplasty, also known as augmentation rhinoplasty or nose reshaping surgery, is a surgical procedure aimed at altering the shape, size, or structure of the nose.
This procedure is commonly performed to enhance the height or definition of the nasal bridge and improve the overall balance of facial features. It often involves augmenting the nose using implants or the patient’s own tissue. The decision to undergo surgery is personal and should be based on an individual’s goals, anatomy, and a clear understanding of the risks involved.
Techniques Used in Asian Rhinoplasty
There are three main surgical approaches for Asian rhinoplasty. The choice of method depends on factors such as the patient’s nasal anatomy, desired outcome, and surgeon’s assessment.
- Nose implant augmentation rhinoplasty
- In this method, a silicone implant is used to enhance the nasal bridge.
- It is the most commonly used approach in many Asian rhinoplasty procedures.
- Autologous cartilage augmentation
- This involves using the patient’s own cartilage, usually harvested from the rib, ear, or nasal septum, to augment and reshape the nose.
- It is used less frequently but can be beneficial in certain cases, such as when additional structural support is needed.
- Combination technique (implant + autologous graft)
- This approach combines a silicone or Gore-Tex implant for the nasal bridge with autologous cartilage grafting to refine the nasal tip.
- It may offer more versatility in reshaping different parts of the nose.
Strengths and Limitations of Silicone Implants
Potential benefits of silicone implants:
- Extensive safety data when used appropriately
- Minimal dissection required, which may result in shorter surgery time and recovery compared to more complex techniques
- Incisions can often be placed inside the nostril, leaving minimal visible scarring
- Does not require cartilage harvesting, so there are no additional donor site scars
- Generally more affordable and can often be performed under local anaesthesia
- Can be removed or replaced if needed
Possible complications and risks:
- Extrusion (implant pushing through the skin): occurs in fewer than 2% of cases when performed by an experienced surgeon, but the risk varies
- Infection: reported in fewer than 3% of cases
- Implant malposition or shifting
- Limited ability to reshape or refine the nasal tip compared to cartilage grafting
- In some individuals, skin discolouration (e.g., redness) may occur if the implant places excessive pressure on the skin or in very cold temperatures
How the Procedure is Performed
The specific technique used will depend on the individual’s anatomy, treatment goals, and overall facial proportions.
- For simple implant augmentation, the procedure is typically done under local anaesthesia and takes about 1 to 1.5 hours.
- For combination augmentation with cartilage grafting and tip refinement, sedation or general anaesthesia is usually required, and the procedure can take 2 to 4 hours.
- Incisions may be made inside the nostril (closed approach) or across the tissue between the nostrils (open approach), depending on the surgical plan.
Recovery Process
- Swelling and bruising are common after surgery, especially during the first 2–3 days.
- Recovery tends to be quicker for procedures involving only an implant and more prolonged when cartilage grafting or open techniques are used.
- Most people can return to light daily activities within 1–2 weeks, but full recovery and resolution of swelling can take several months.
- Following Dr Xu’s post-operative care instructions is important to reduce complications and support healing.
Other Non-Surgical Options
For individuals seeking less invasive nose contouring, non-surgical approaches may be considered:
- Facial volume treatments: temporary injectable treatments to enhance nasal definition or smooth contours
- Fat transfer: uses fat from the patient’s own body to subtly enhance nasal shape
These options do not produce permanent changes and carry their own risks, which should be discussed during a consultation.
Risks and Complications of Asian Rhinoplasty
As with all surgical procedures, rhinoplasty carries risks. These may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Implant malposition or extrusion
- Scarring
- Asymmetry or uneven results
- Breathing difficulties
- Allergic reaction to materials or medications
- Revision surgery if the initial outcome is unsatisfactory
A qualified surgeon will explain these risks in detail before you decide whether to proceed.
Important Considerations
- Asian rhinoplasty is a cosmetic, elective procedure and is not medically necessary.
- Under Medical Board of Australia guidelines, there is a mandatory 7-day cooling-off period for adults before cosmetic surgery can proceed.
- Individuals under 18 years of age must undergo a psychological assessment before being considered for surgery.
- A face-to-face consultation with a registered specialist is required to assess suitability, discuss treatment options, risks, and expected outcomes.
- Results vary between individuals, and no specific aesthetic outcome can be guaranteed.
